
- Create proceses

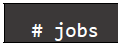
- Lists the jobs running in the background, giving the job number
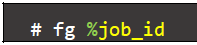
- Bring a background job to the foreground
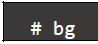
- Change suspend the current foreground job to background
- nohup command: when using the command shell , prefixing a command with nohup being aborted automatically when you log out or exit the shell

- Kill processes: Signals are software interrupts. They provide a way for user (or a process) to directly communicate with a process. Signals can be sent with the kill command

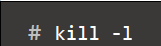
- List of signals
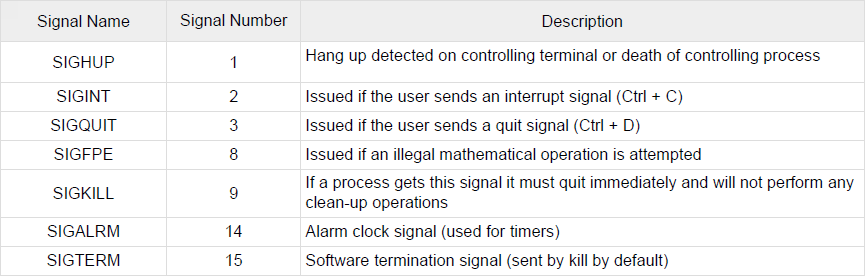
- killall command: sends a signal to all processes running any of the specifies command. If no signal name is specifies, SIGTERM is sent

- pgrep and pkill command: looks through the currently running processes and lists the process IDs which matches the selection criteria to stdout

- screen command: It creates a single window with a shell in it (or the specified command) and then gets out of your way so that you can use the program as you normally would
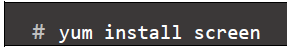
- Install screen package
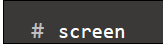
- Start screen
- Start screen with session name (description for screen session)

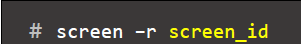
- Restore screen
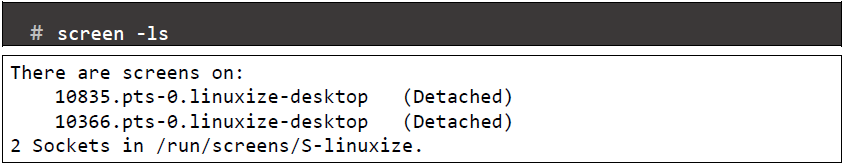
- List all screen session
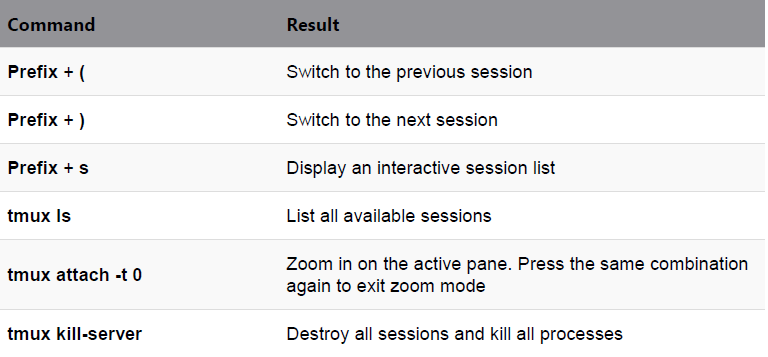
- tmux command: a terminal multiplexer. It lets you switch easily between several programs in one terminal, detach them (they keep running in the background) and reattach them to a different terminal
- Install tmux package
- Start new tmux session
- Start tmux with session name (description for screen session)

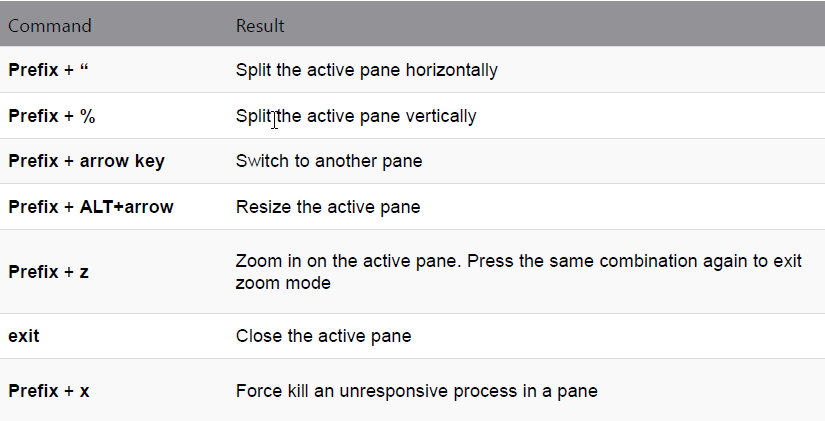
- Prefix will be used to refer to either the default CTRL+b

- screen command
- Method 1: “Ctrl-A” and “d” to detach the screen
- Method 2: Terminated screen
- Kill the screen: Use “Ctrl-A” and “K”
- Kill all process with vi command
- Use to pkill
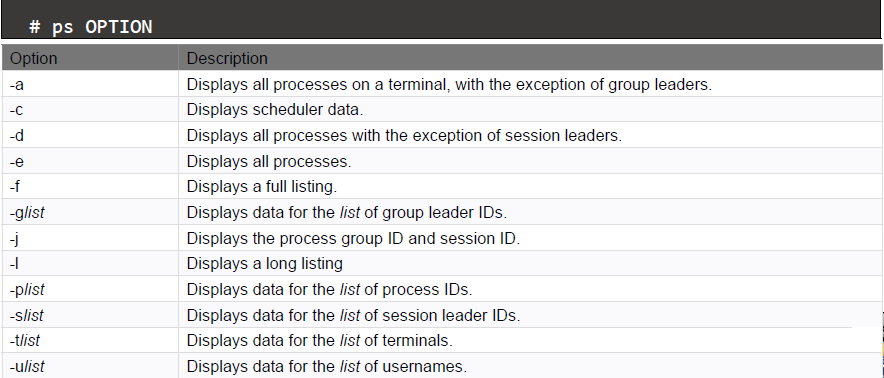
- ps command is the classic Unix/Linux command to list processes and their details
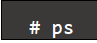
- with no arguments, ps lists the processes associated with the current terminal
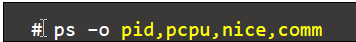
- The columns that are displayed can be customized. For example
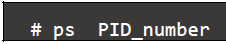
- To view details of a specific process using its PID
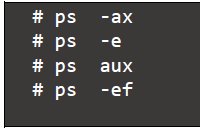
- View all processes on your system
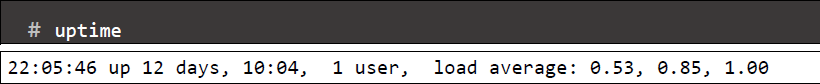
- uptime command: Tell how long the system has been running
- free command: Display amount of free and used memory in the system


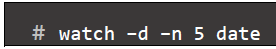
- watch command: displaying its output and errors (the first screenfull). This allows you to watch the program output change over time. By default, the program is run every 2 seconds. By defaults, watch will run until interrupted
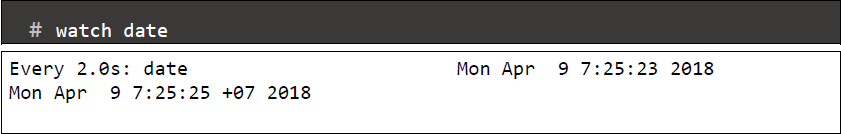
- Highlight different between updates
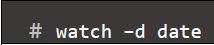
- Customize update interval
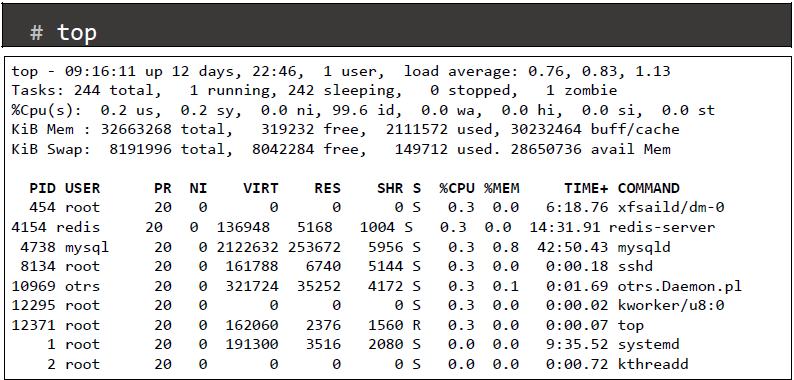
- top command provides a dynamic real-time view of a running system
** If you have difficulty in configuring Sophos products in Viet Nam, please contact us:
Hotline: 02862711677
Email: info@thegioifirewall.com
Leave a Reply