
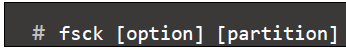
- fsck command: is used to check and repair Linux filesystems (ext2, ext3, ext4, etc.)
The exit code returned by fsck is the sum of the following condition

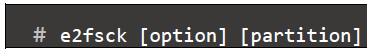
- e2fsck command: is used to check the ext2/ext3/ext4 family of file system
Should be root to execute this command
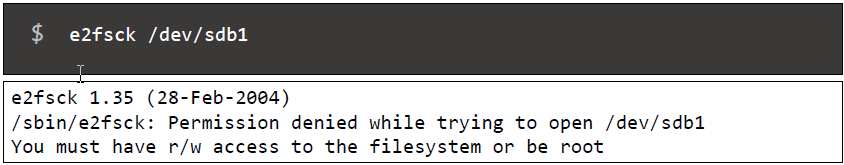
If the file system mounted, you’ll get the following error message

Using -p option, you can instruct e2fsck to check and automatically repair all issues without prompting you for comfirmation

Using -y option, which will use “yes” answer to all the questions that are asked by the e2fsck command

Using -n option, you can instruct e2fsck to perform check only. i.e this will not make any changes to the filesystem, it will only check

Using ‘-C 0‘ option, it will display a progress bar while e2fsck is doing the check

- tune2fs command: adjust tunable filesystem parameters on ext2/ext3/ext4 filesystems
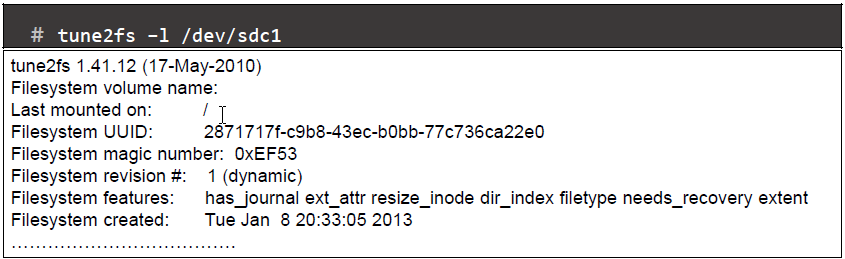
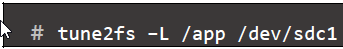
Set volume Label
Using -j option to convert ext2 to ext3 file system

Using -O option to convert ext3 to ext4 file system

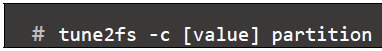
Set maximum mount count (after that, filesystem will be checked by e2fsck command)
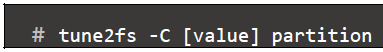
Change the current mount count to <value>
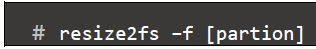
- resize2fs command: will resize ext2, ext3 or ext4 file systems. It can be used to enlarge or shrink an unmounted file system located on device. If the filesystem is mounted, it can be used to expand the size of the mounted filesystem, assuming the kernel supports on-line resizing
- An XFS file system may be grown while mounted using the xfs_growfs command

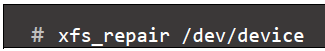
- To repair an XFS file system
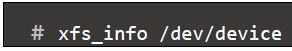
- Displays geometry information about an existing XFS filesystem
** If you have difficulty in configuring Sophos products in Viet Nam, please contact us:
Hotline: 02862711677
Email: info@thegioifirewall.com
Leave a Reply